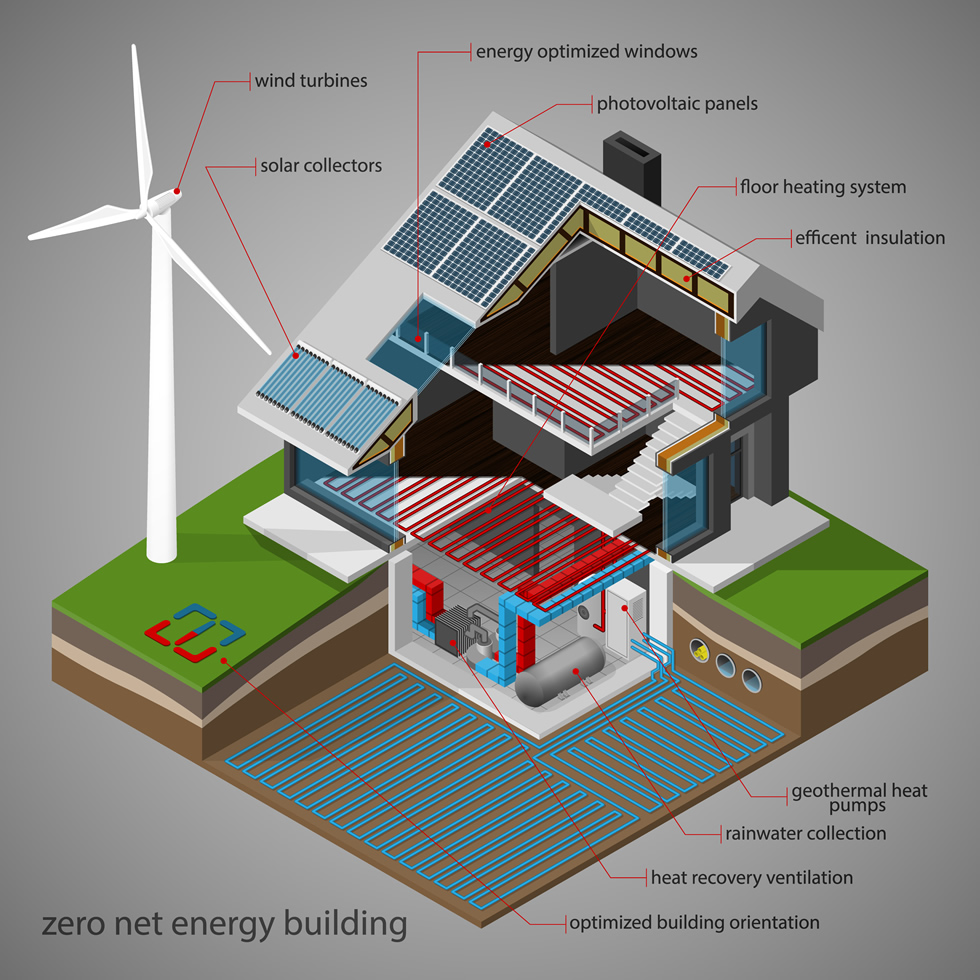
Net-Zero Energy Building
A Zero Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero Energy (NZE) building, or a Zero Net Energy (ZNE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site.
These buildings contribute less overall greenhouse gas to the atmosphere during operations than similar non-ZNE buildings.
Advantages
- Isolation for building owners from future energy price increases
- Increased comfort due to more-uniform interior temperatures.
- Reduced total cost of ownership due to improved energy efficiency
- Reduced total net monthly cost of living.
- Reduced risk of loss from grid blackouts.
Disadvantages
- Initial costs can be higher – effort required to understand, apply, and qualify for ZEB subsidies, if they exist.
- Very few designers or builders have the necessary skills or experience to build ZEBs
- Possible declines in future utility company renewable energy costs may lessen the value of capital invested in energy efficiency.
- ZEB is not free of carbon emissions, glass has a high embodied energy, and the production requires a lot of carbon.

Comments
Post a Comment